Monitoring ArgoCD Deployments with Prometheus and OpenObserve


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For FreeArgo CD is a leading open-source declarative GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. With over 14,000 GitHub stars and a growing community, it has become the de facto standard for implementing GitOps workflows. GitOps is a paradigm where the desired state of your infrastructure is defined in Git repositories, and automated processes ensure the actual state matches this definition.
In the GitOps model implemented by Argo CD:
Argo CD implements these principles through three main components:
As organizations adopt Argo CD for production workloads, monitoring becomes crucial for ensuring reliability and performance.
Argo CD exposes Prometheus metrics from several components:
Some of the most critical metrics to monitor include:
argocd_app_info: Information about applications with labels for sync status and health statusargocd_app_reconcile: Application reconciliation performance in secondsargocd_app_sync_total: Counter for application sync historyargocd_git_request_total: Number of git requests performedargocd_cluster_connection_status: The Kubernetes cluster connection statusFirst, let's verify that Argo CD services are running and exposing metrics:
kubectl get svc -n argocd
The output should show various Argo CD services including:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
argocd-applicationset-controller ClusterIP 172.20.19.231 <none> 7000/TCP,8080/TCP 359d
argocd-metrics ClusterIP 172.20.112.153 <none> 8082/TCP 359d
argocd-notifications-controller-metrics ClusterIP 172.20.194.56 <none> 9001/TCP 359d
argocd-redis-ha-haproxy ClusterIP 172.20.162.192 <none> 6379/TCP,9101/TCP 359d
argocd-repo-server ClusterIP 172.20.39.109 <none> 8081/TCP,8084/TCP 359d
argocd-server-metrics ClusterIP 172.20.26.5 <none> 8083/TCP 359d
Check that metrics annotations are properly set in your Argo CD deployments:
kubectl get deployment argocd-redis-ha-haproxy -n argocd -o yaml | grep -A 10 annotations
You should see annotations like:
annotations:
prometheus.io/path: /metrics
prometheus.io/port: "9101"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
If metrics annotations are missing, you may need to update your Argo CD deployment manifests to include them:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: argocd-redis-ha-haproxy
# ...
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/path: /metrics
prometheus.io/port: "9101"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
You can verify that metrics are being exposed by port-forwarding to the respective services:
# For Application Controller metrics
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-metrics -n argocd 8082:8082
In another terminal
curl http://localhost:8082/metrics
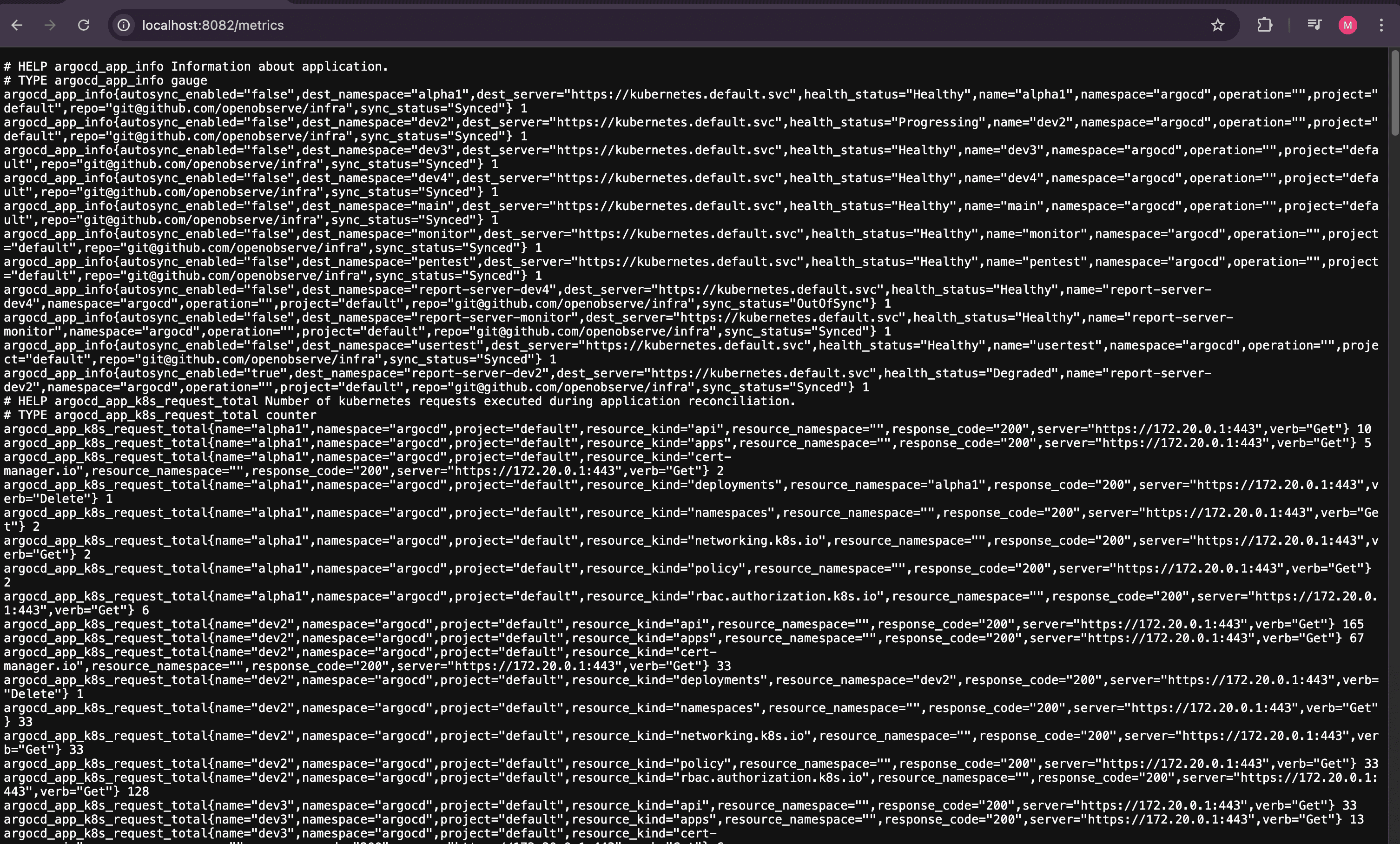
The most efficient way to collect Argo CD metrics and forward them to OpenObserve is by using the OpenObserve Collector. This collector is based on OpenTelemetry and can be deployed as a DaemonSet in your Kubernetes cluster.
Note: You can find the below steps in the "Data Sources" section as well once you log in to OpenObserve.
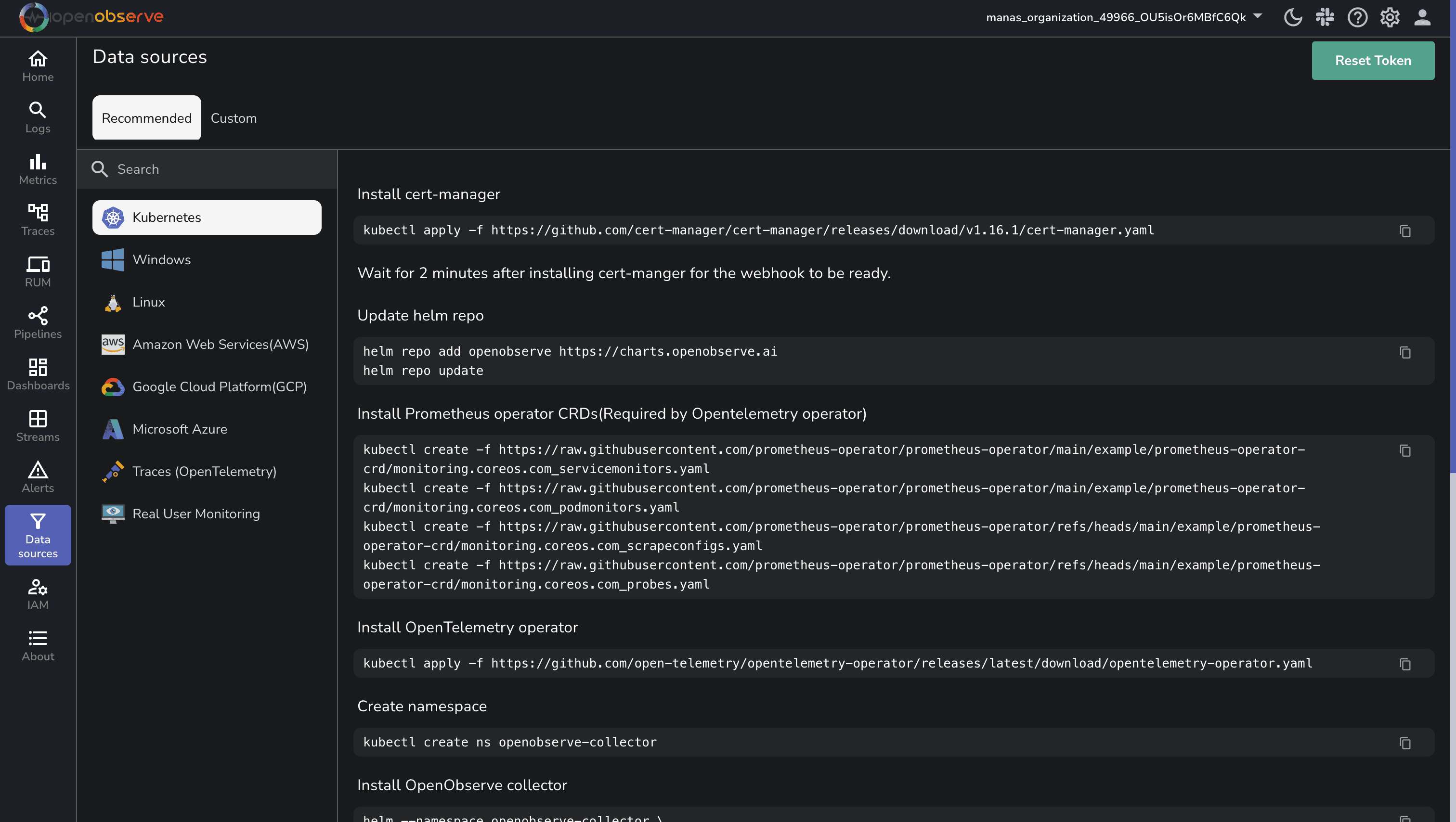
Cert-Manager is a tool to automate the management of TLS certificates within Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.13.1/cert-manager.yaml
Cert-Manager will handle the certificates and ensure secure connections between services.
Add the OpenObserve Helm repository to make the OpenObserve components available for installation:
helm repo add openobserve https://charts.openobserve.ai
helm repo update
Helm makes it easy to deploy and manage OpenObserve components in your Kubernetes cluster.
The Prometheus Operator manages Kubernetes monitoring components like ServiceMonitors and PodMonitors:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator/main/example/prometheus-operator-crd/monitoring.coreos.com_servicemonitors.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator/main/example/prometheus-operator-crd/monitoring.coreos.com_podmonitors.yaml
This step is essential for monitoring pods and services and pushing their metrics to OpenObserve.
OpenTelemetry Operator is an open-source observability tool designed to collect, process, and export metrics and logs from Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-operator/releases/latest/download/opentelemetry-operator.yaml
The OpenTelemetry Operator will be responsible for collecting telemetry data (logs, metrics, and traces) from your Kubernetes cluster.
To isolate the OpenObserve collector deployment, create a separate namespace:
kubectl create ns openobserve-collector
This step helps organize resources and manage permissions more effectively.
Now, install the OpenObserve collector using Helm:
# Copy the below command from the Data Sources section of OpenObserve
# once you login, that will provide you with prefilled auth_token
helm --namespace openobserve-collector \
install o2c openobserve/openobserve-collector \
--set exporters."otlphttp/openobserve".endpoint=https://api.openobserve.ai/api/default \
--set exporters."otlphttp/openobserve".headers.Authorization="Basic <auth_token>" \
--set exporters."otlphttp/openobserve_k8s_events".endpoint=https://api.openobserve.ai/api/default \
--set exporters."otlphttp/openobserve_k8s_events".headers.Authorization="Basic <auth_token>"
This command configures the OpenObserve collector to use the OTLP HTTP exporter to send logs and metrics directly to the specified OpenObserve endpoint. Ensure the provided authorization token is secure and base64-encoded.
Once the installation is complete, check if the pods are running successfully:
kubectl get pods -n openobserve-collector
You should see OpenObserve Collector pods in the Running state. If not, inspect the logs to diagnose issues:
kubectl logs -f <pod-name> -n openobserve-collector
After deploying the OpenObserve collector, we need to modify its configuration to collect metrics from Argo CD.
First, let's get the current values used by the collector:
helm get values o2c -n openobserve-collector -o yaml > current-values.yaml
Now, add the Prometheus receiver for Argo CD to the configuration file (current-values.yaml). You'll need to add or update the prometheus receiver under the agent.receivers section:
agent:
receivers:
prometheus:
config:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: otel-collector
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets:
- 0.0.0.0:8888
# Argo CD metrics scraping configuration
- job_name: argocd-metrics
scrape_interval: 15s
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
namespaces:
names:
- argocd
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
regex: 'argocd-metrics|argocd-server-metrics|argocd-repo-server|argocd-applicationset-controller|argocd-redis-ha-haproxy|argocd-notifications-controller-metrics'
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_port_name]
regex: 'metrics|http-exporter-port'
action: keep
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
target_label: service
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
target_label: pod
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
target_label: namespace
Also, make sure that the prometheus receiver is included in the metrics pipeline under agent.service.pipelines.metrics.receivers:
agent:
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers:
- kubeletstats
- hostmetrics
- prometheus # Make sure this is included
After modifying the configuration, apply it using Helm:
helm upgrade o2c openobserve/openobserve-collector \
-f current-values.yaml \
-n openobserve-collector
Check if the new configuration is applied by looking at the logs:
kubectl logs -n openobserve-collector -l app.kubernetes.io/name=openobserve-collector
Look for entries related to scraping Argo CD metrics to confirm the configuration is working.
You can enable additional metrics by modifying the Argo CD Application Controller.
To expose Argo CD application labels as Prometheus metrics:
kubectl patch statefulset argocd-application-controller -n argocd --type=json -p='[
{
"op": "add",
"path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-",
"value": "--metrics-application-labels=team-name"
},
{
"op": "add",
"path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-",
"value": "--metrics-application-labels=business-unit"
}
]'
Similarly, to expose application conditions as metrics:
kubectl patch statefulset argocd-application-controller -n argocd --type=json -p='[
{
"op": "add",
"path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-",
"value": "--metrics-application-conditions=OrphanedResourceWarning"
},
{
"op": "add",
"path": "/spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-",
"value": "--metrics-application-conditions=ExcludedResourceWarning"
}
]'
Once the OpenObserve Collector is running, you can verify that metrics are being collected by:
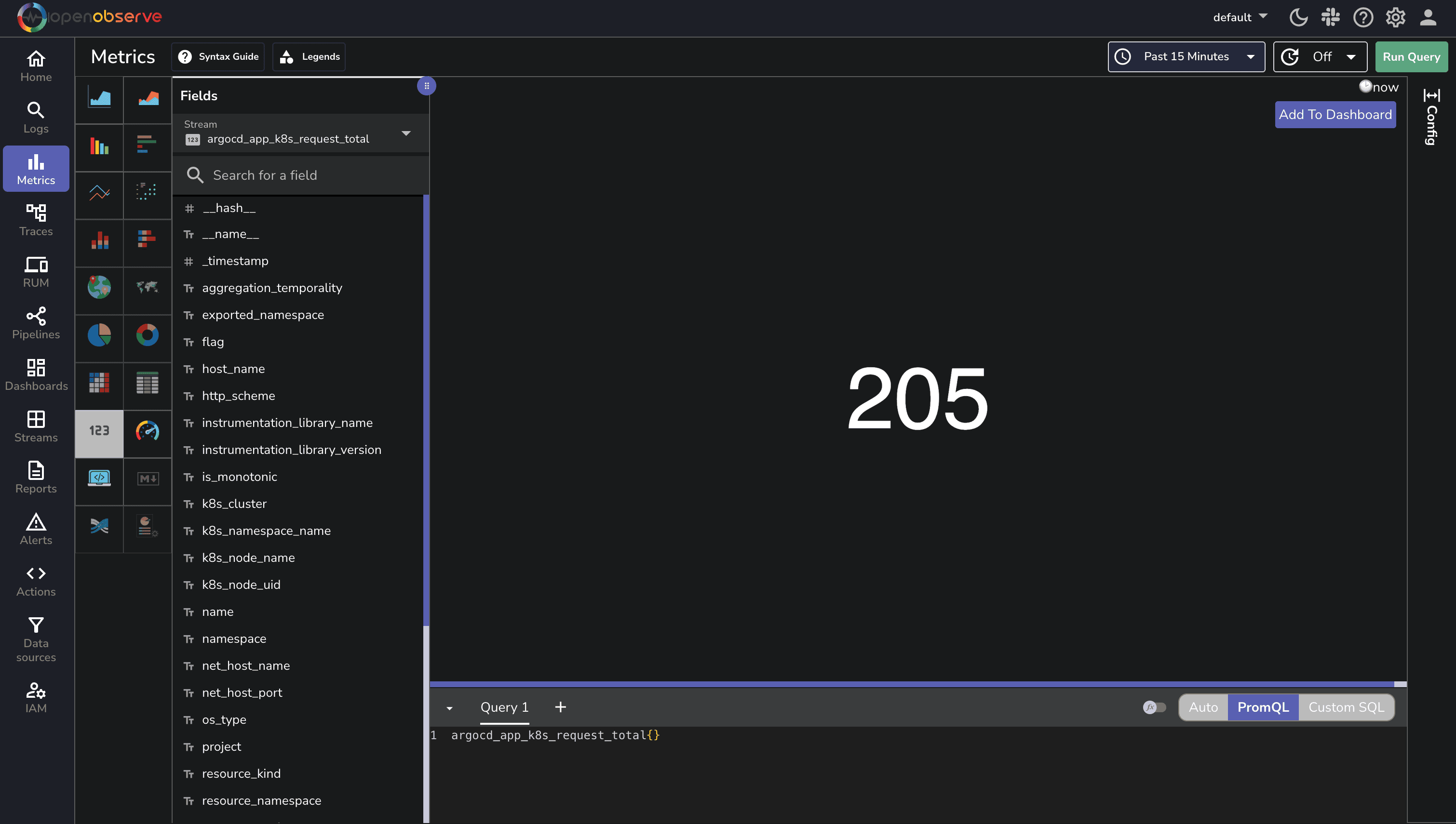 3. Check for other Argo CD metrics like
3. Check for other Argo CD metrics like argocd_git_request_total
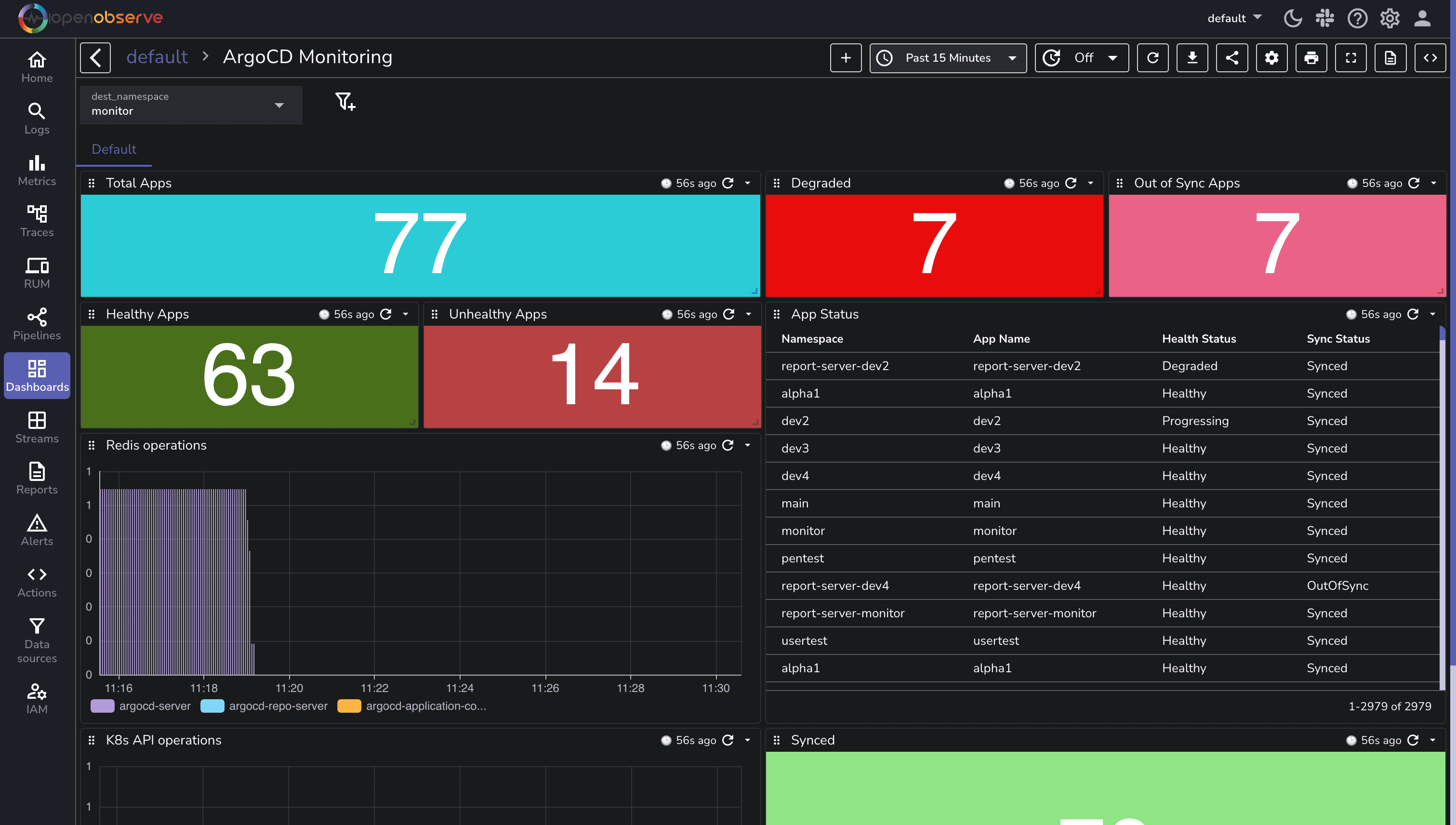
Here is a pre-built ArgoCD metrics monitoring dashboard that you can directly import into your OpenObserve instance. Simply navigate to the Dashboards section and click on "Import Dashboard" to access this ready-to-use monitoring solution.
If metrics aren't appearing in OpenObserve, check:
kubectl logs -n openobserve-collector -l app.kubernetes.io/name=openobserve-collector
By following this guide, you've set up monitoring for your Argo CD installation using OpenObserve and OpenTelemetry. This approach provides a scalable and cloud-native way to monitor your GitOps deployment pipeline.
Next steps after setting up this monitoring solution:
The beauty of this approach is that you're using the same OpenTelemetry standard for both your applications and infrastructure components, creating a unified observability stack.
Happy monitoring! 🚀