Why Stream Cloudflare Logs?


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For Free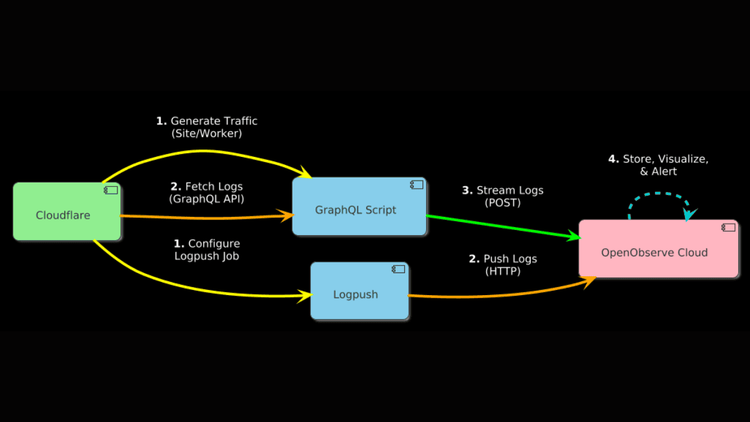
Cloudflare protects and optimizes millions of domains with its CDN, DDoS protection, and DNS services. Its logs, packed with HTTP request data, response codes, and security events, are vital for monitoring web performance and threats. While Logpush provides real-time log streaming for Enterprise plans, it’s not the only way to capture Cloudflare logs—or a requirement. This guide equips Free, Pro, Business, and Enterprise users with two practical methods to stream Cloudflare logs: the GraphQL API (accessible to all plans) or Logpush (Enterprise-only).
In this article, we’ll show you how to set up Cloudflare logs streaming to OpenObserve using real traffic from a website or Worker. Whether you’re avoiding Logpush costs or enhancing an Enterprise setup, you’ll have it running in 30 minutes. Let’s get started!
Streaming Cloudflare logs delivers immediate, actionable insights into your web traffic—far surpassing static exports. Here’s what it enables:
For Free, Pro, and Business users, streaming Cloudflare logs offers a no-cost alternative to Logpush. For Enterprise users, it’s a versatile enhancer or standalone option, reducing reliance on premium features. OpenObserve simplifies the process, making Cloudflare logs streaming accessible and efficient—here’s how to implement it.
You’ll need:
To stream Cloudflare logs, you will first need to grab your OpenObserve Cloud endpoint and credentials. Log into OpenObserve and follow these steps:
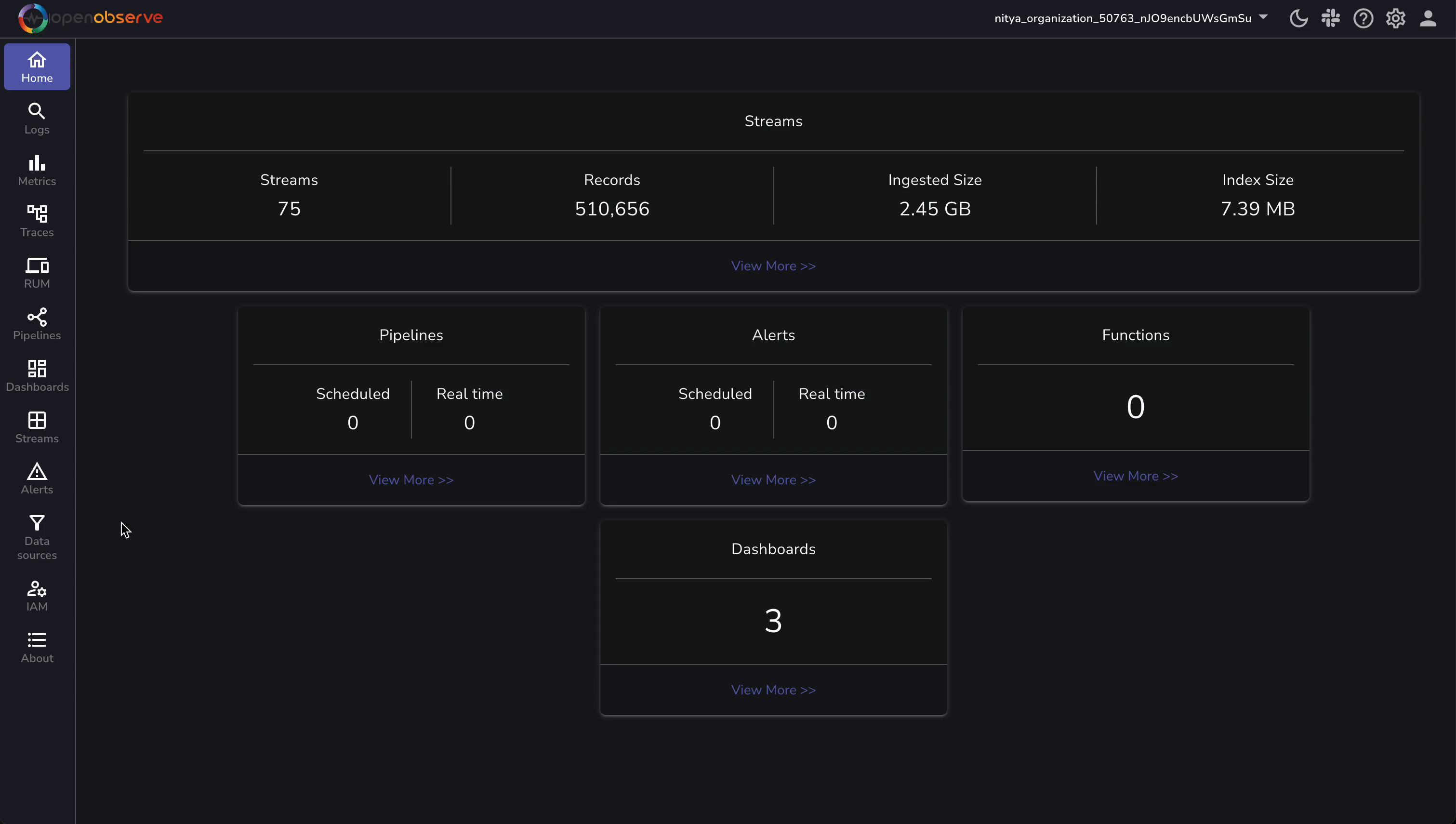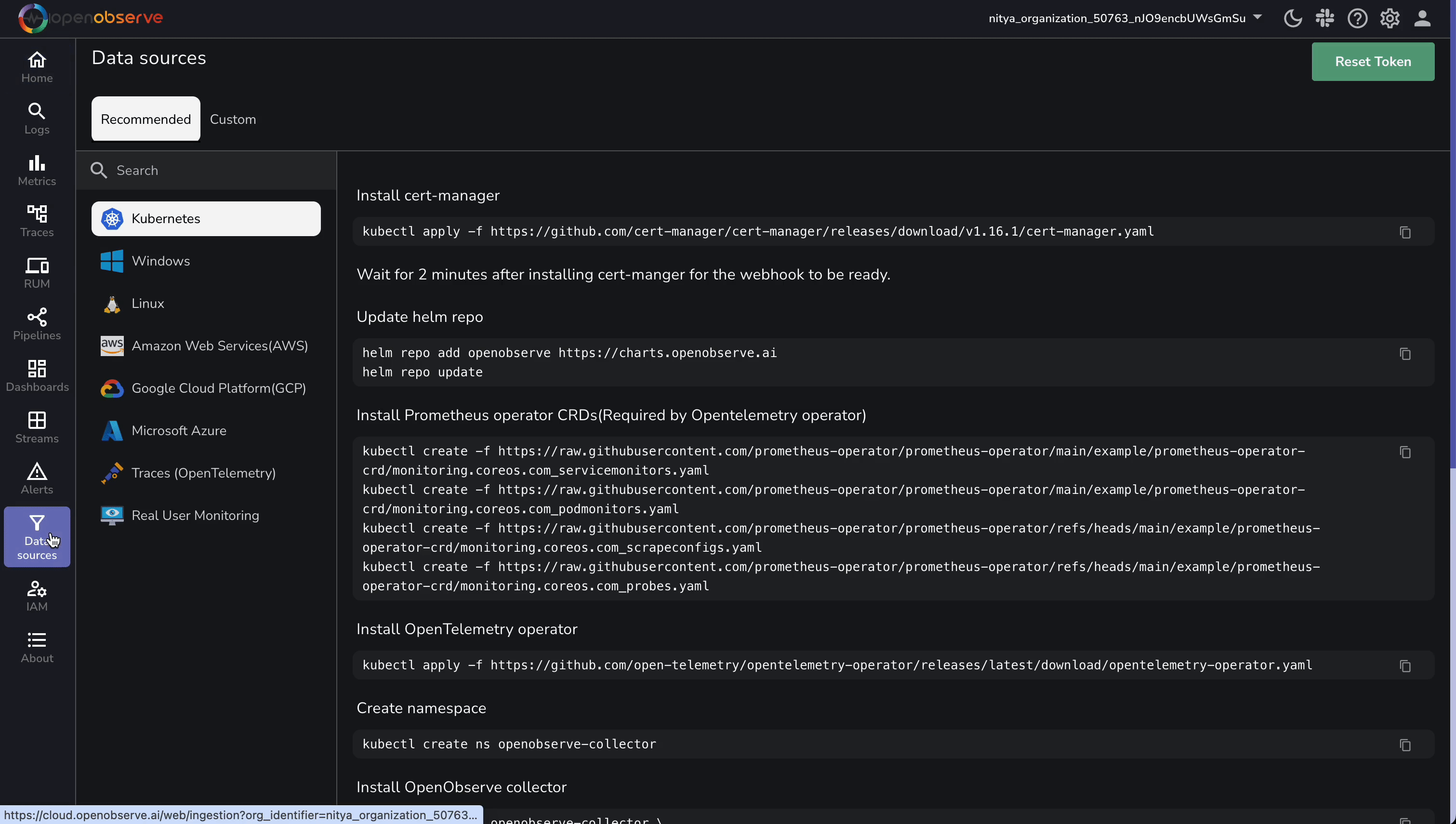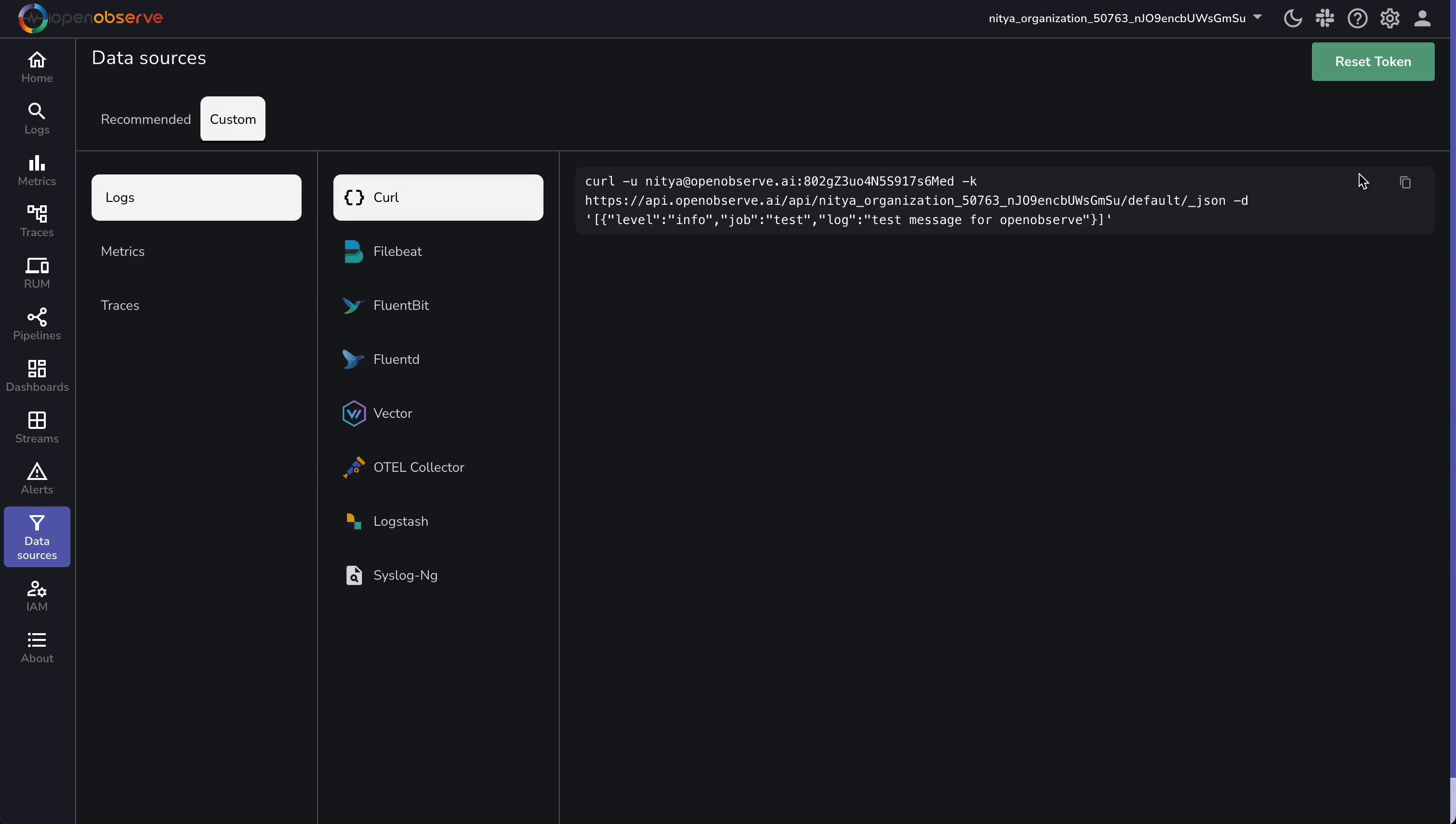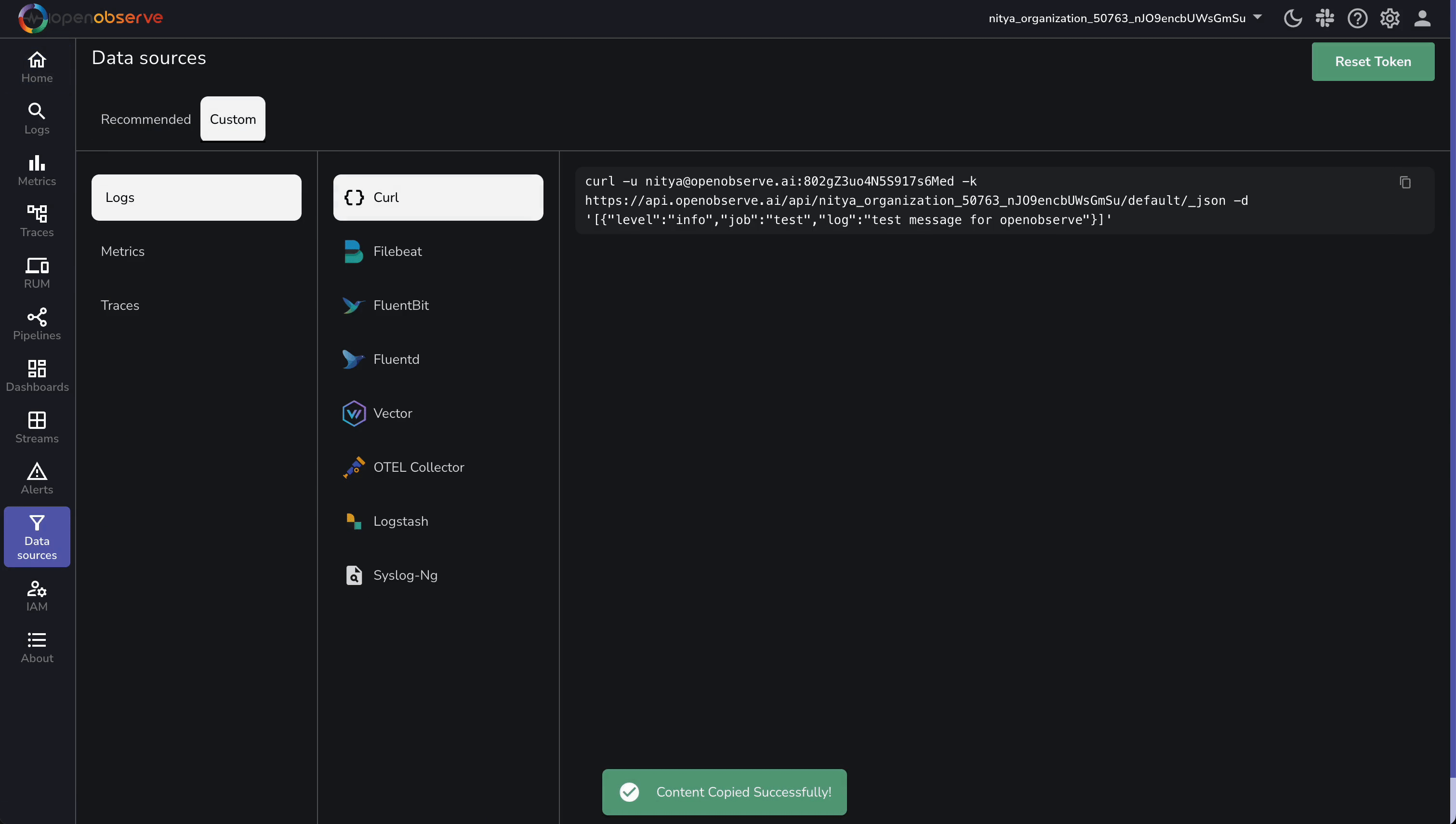
https://api.openobserve.ai/api/<your_organization_id>cloudflare_logs/_json (replace <your_organization_id>; update default to cloudflare_logs). Replace the example values with yours. Your OpenObserve setup is ready—on to the next step!
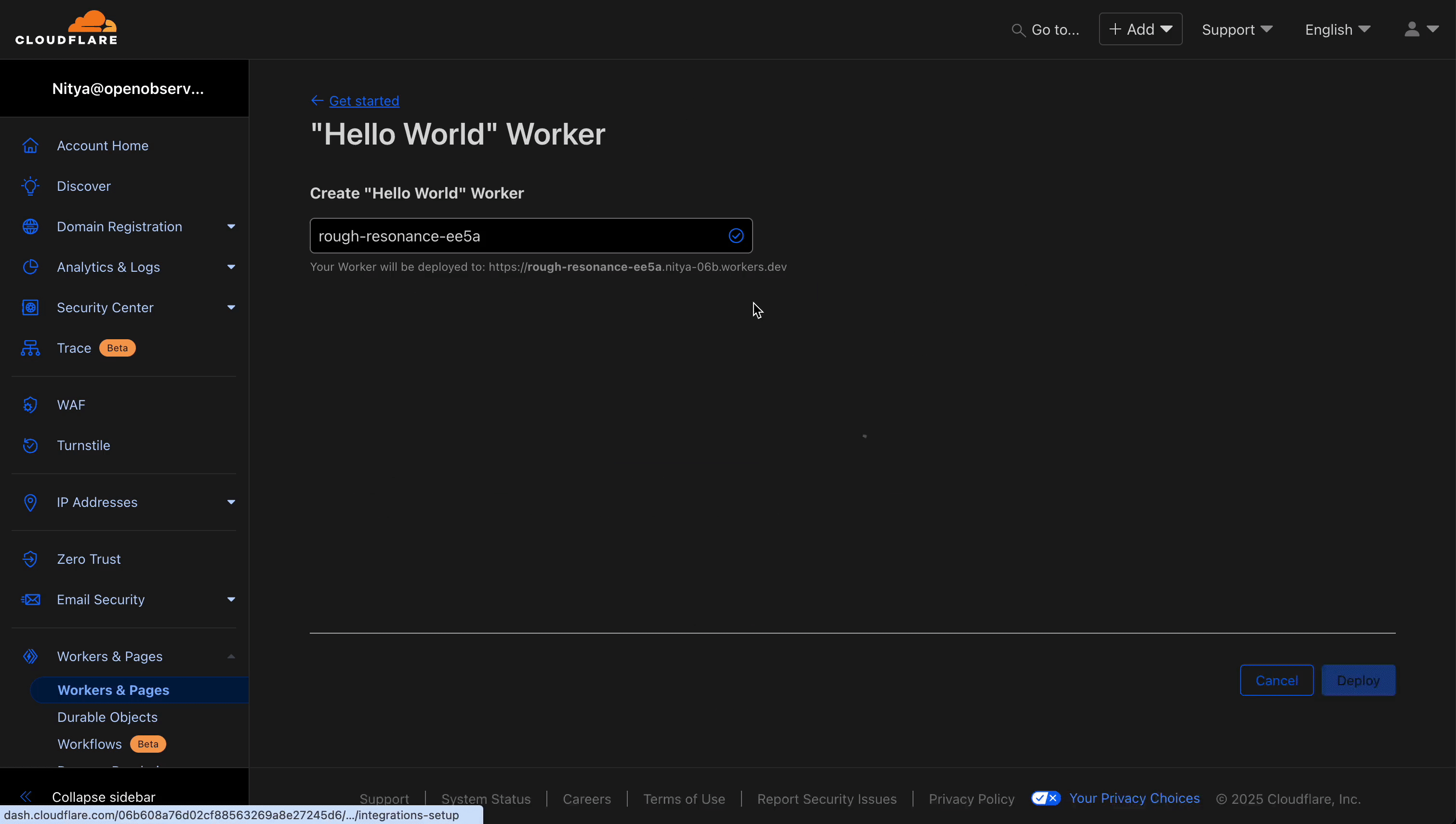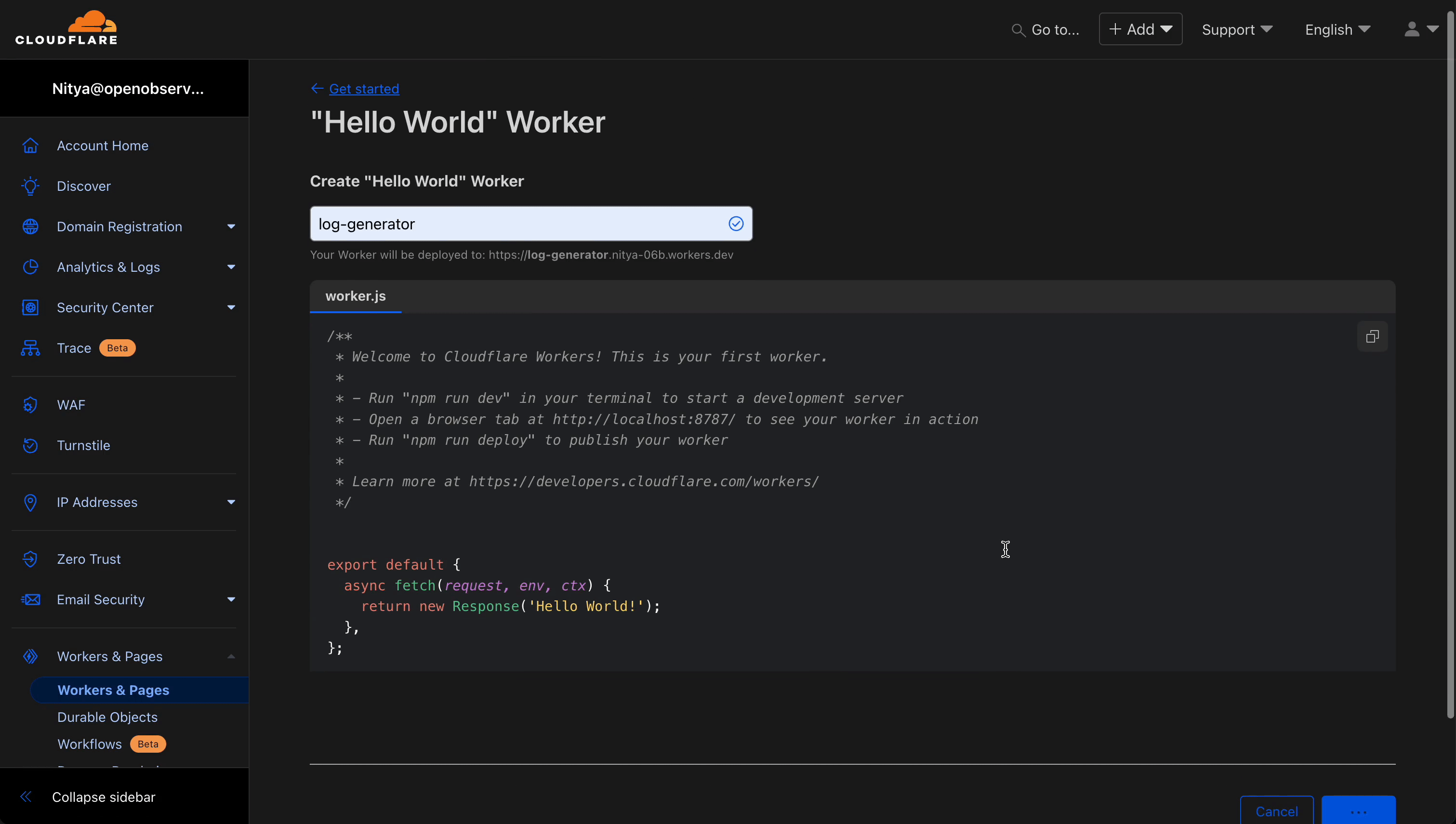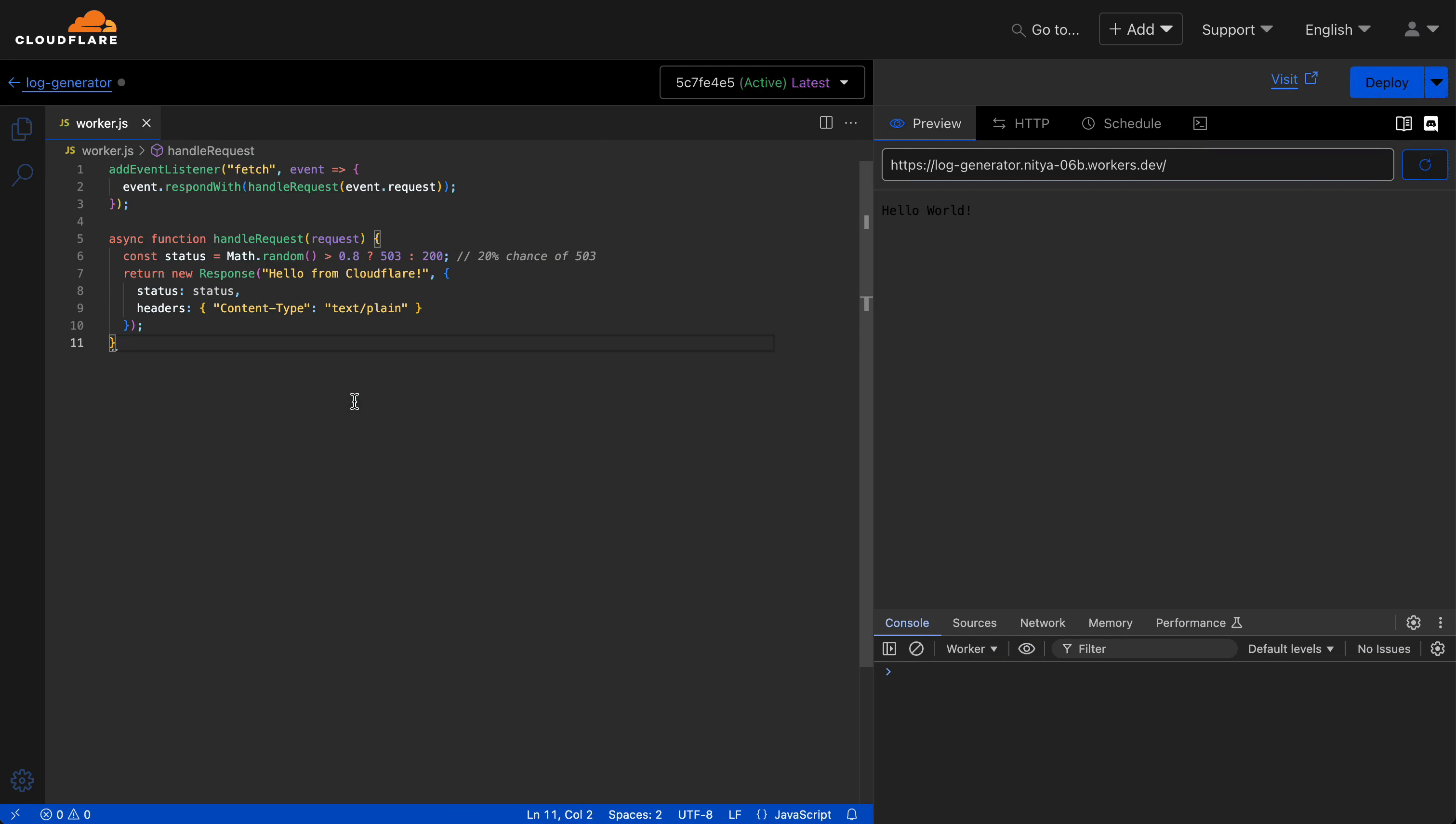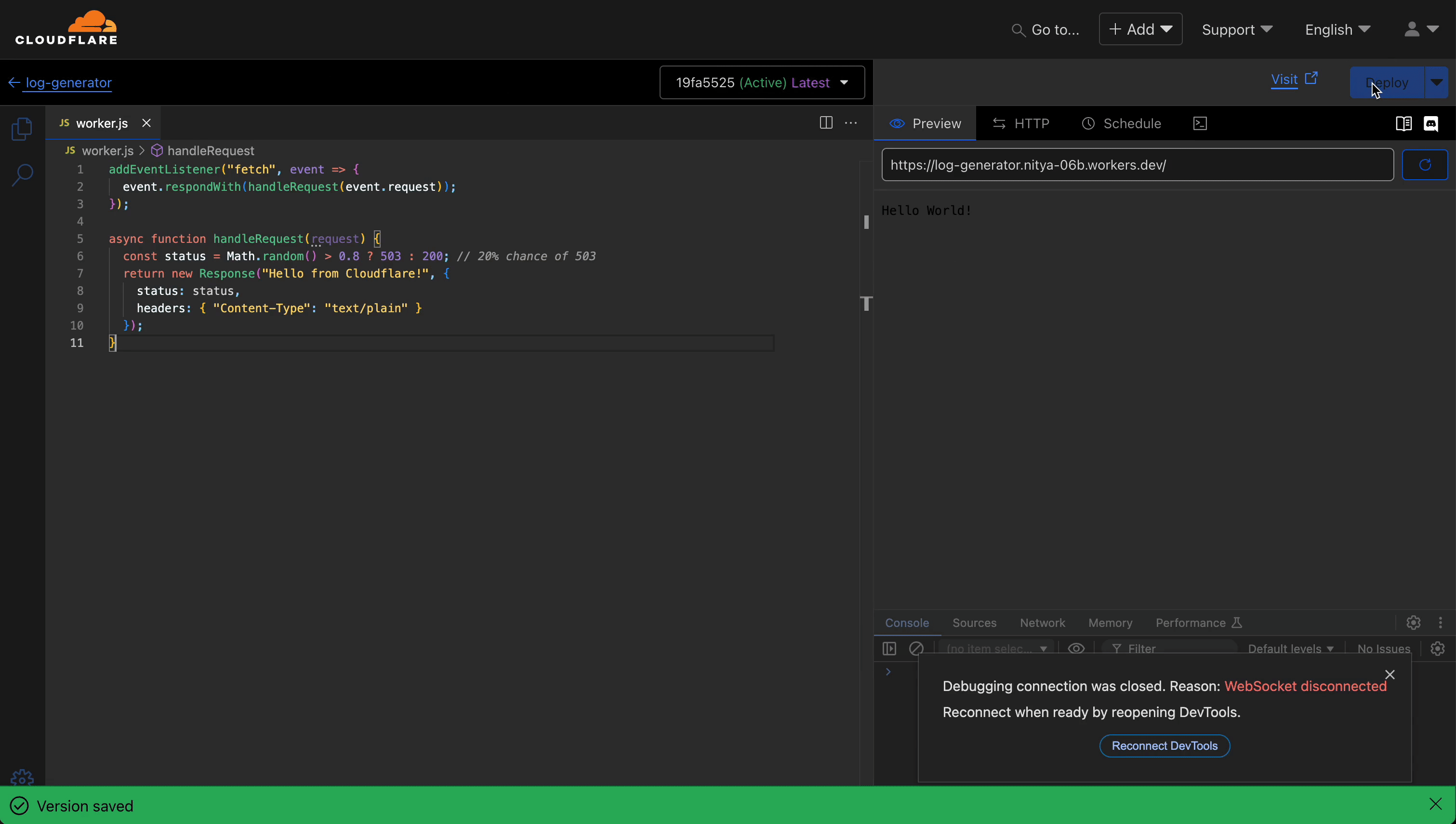
Real logs come from actual traffic—no artificial loops required. Choose a scenario:
addEventListener("fetch", event => {
event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request));
});
async function handleRequest(request) {
const status = Math.random() > 0.8 ? 503 : 200; // 20% chance of 503
return new Response("Hello from Cloudflare!", {
status: status,
headers: { "Content-Type": "text/plain" }
});
}
Choose one of these options to stream your logs—both integrate seamlessly:
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
pip install requests
import requests
import time
import json
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone
import base64
import random
## Cloudflare config
API_TOKEN = "xUL39zImSqAG5-JJNpLMC7HVIqGuckorb9AKo-Tx" # Your token
EMAIL = "your-username@example.com" # Your email
ZONE_IDS = [] # Leave empty for all zones, or add ["zone_id_1"]
## OpenObserve config
OPENOBSERVE_URL = "https://api.openobserve.ai/api/your_organization_id/cloudflare_logs/_json"
OPENOBSERVE_USER = "your-username@example.com"
OPENOBSERVE_PASS = "your_password" # Your password
def simulate_cloudflare_logs():
methods = ["GET", "POST", "PUT"]
uris = ["/", "/api/users", "/checkout"]
statuses = [200, 404, 429, 503]
countries = ["US", "IN", "UK"]
return [{
"dimensions": {
"datetime": datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat(),
"clientRequestHTTPMethodName": random.choice(methods),
"clientRequestURI": random.choice(uris),
"edgeResponseStatus": random.choice(statuses),
"clientCountryName": random.choice(countries)
},
"sum": {
"bytes": random.randint(100, 5000),
"requests": random.randint(1, 5)
}
} for _ in range(random.randint(1, 5))]
def fetch_cloudflare_logs(zone_ids):
url = "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/graphql"
headers = {
"X-Auth-Email": EMAIL,
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
end_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
start_time = end_time - timedelta(minutes=5)
zone_filter = f'zoneTag: "{zone_ids[0]}"' if zone_ids else ""
query = """
{
viewer {
zones(%s) {
httpRequests1mGroups(limit: 1000, filter: {datetime_geq: "%s", datetime_leq: "%s"}) {
dimensions {
datetime
clientRequestHTTPMethodName
clientRequestURI
edgeResponseStatus
clientCountryName
}
sum {
bytes
requests
}
}
}
}
}
""" % ("filter: {%s}" % zone_filter if zone_filter else "",
start_time.isoformat(), end_time.isoformat())
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json={"query": query})
if response.status_code != 200:
print(f"API Error: {response.status_code} - {response.text}")
return simulate_cloudflare_logs()
try:
data = response.json()
if not data or not data.get("data", {}).get("viewer", {}).get("zones"):
print("No logs yet—waiting for traffic. Using simulated data.")
return simulate_cloudflare_logs()
logs = []
for zone in data["data"]["viewer"]["zones"]:
logs.extend(zone["httpRequests1mGroups"])
return logs
except (json.JSONDecodeError, AttributeError):
print("API response issue. Switching to simulation.")
return simulate_cloudflare_logs()
def send_to_openobserve(logs):
if not logs:
print("No logs to send.")
return
auth_str = base64.b64encode(f"{OPENOBSERVE_USER}:{OPENOBSERVE_PASS}".encode()).decode()
headers = {"Authorization": f"Basic {auth_str}"}
payload = [log["dimensions"] | log["sum"] for log in logs]
response = requests.post(OPENOBSERVE_URL, headers=headers, json=payload)
print(f"Sent {len(payload)} logs at {datetime.now(timezone.utc)}: {response.status_code}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Streaming Cloudflare logs to OpenObserve...")
while True:
try:
logs = fetch_cloudflare_logs(ZONE_IDS)
send_to_openobserve(logs)
time.sleep(60) # Poll every minute
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
logs = simulate_cloudflare_logs()
send_to_openobserve(logs)
time.sleep(60)
python cloudflare_logs_to_openobserve.py
https://api.openobserve.ai/api/your_organization_id/cloudflare_logs/_json
echo -n "your-username@example.com:802gZ3uo4N5S917s6Med" | base64
Check OpenObserve:
{
"_timestamp": 1742220353596180,
"bytes": 2109,
"clientcountryname": "IN",
"clientrequesthttpmethodname": "POST",
"clientrequesturi": "/",
"datetime": "2025-03-17T14:05:53.447689+00:00",
"edgeresponsestatus": 503,
"requests": 1
}
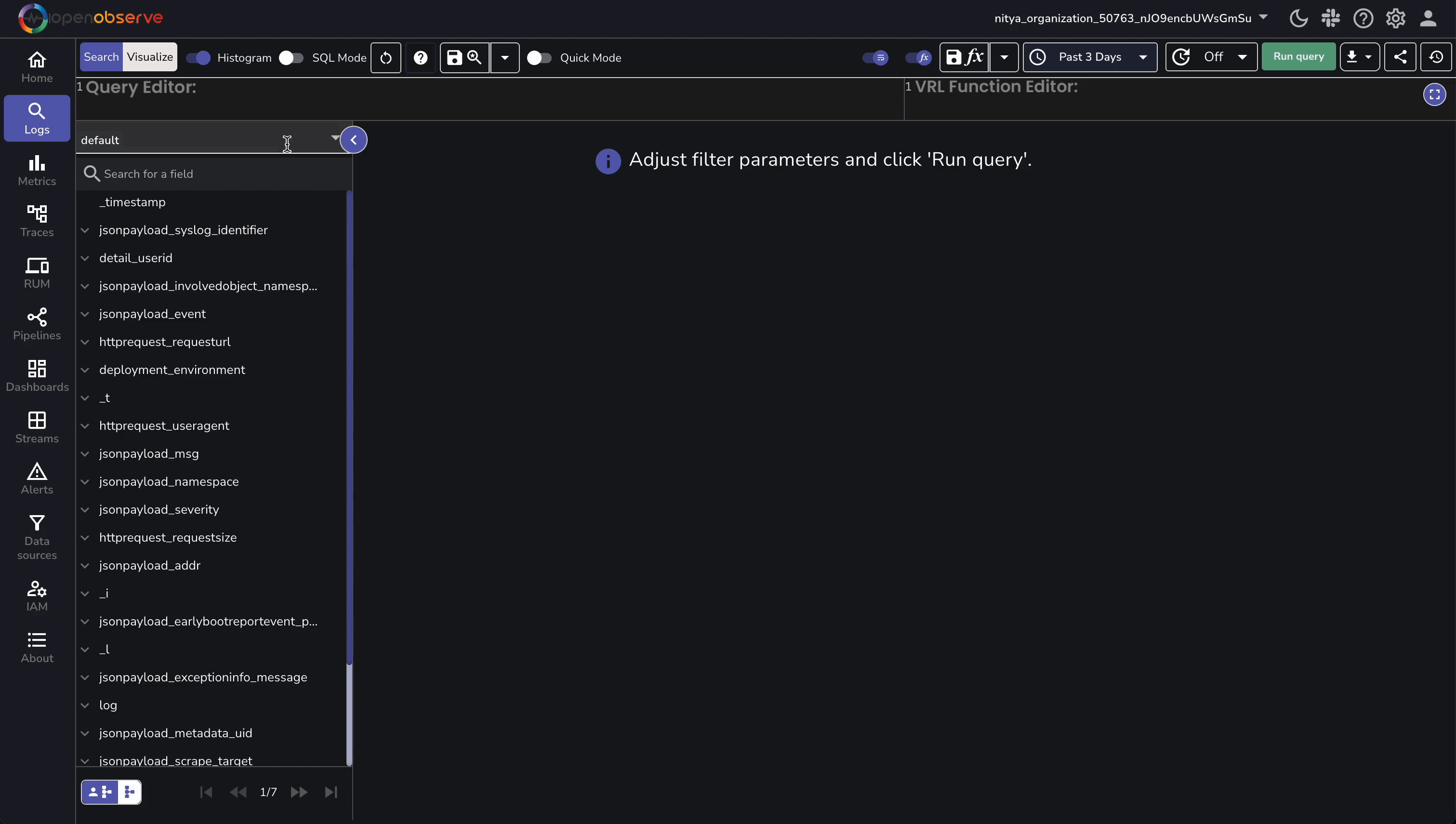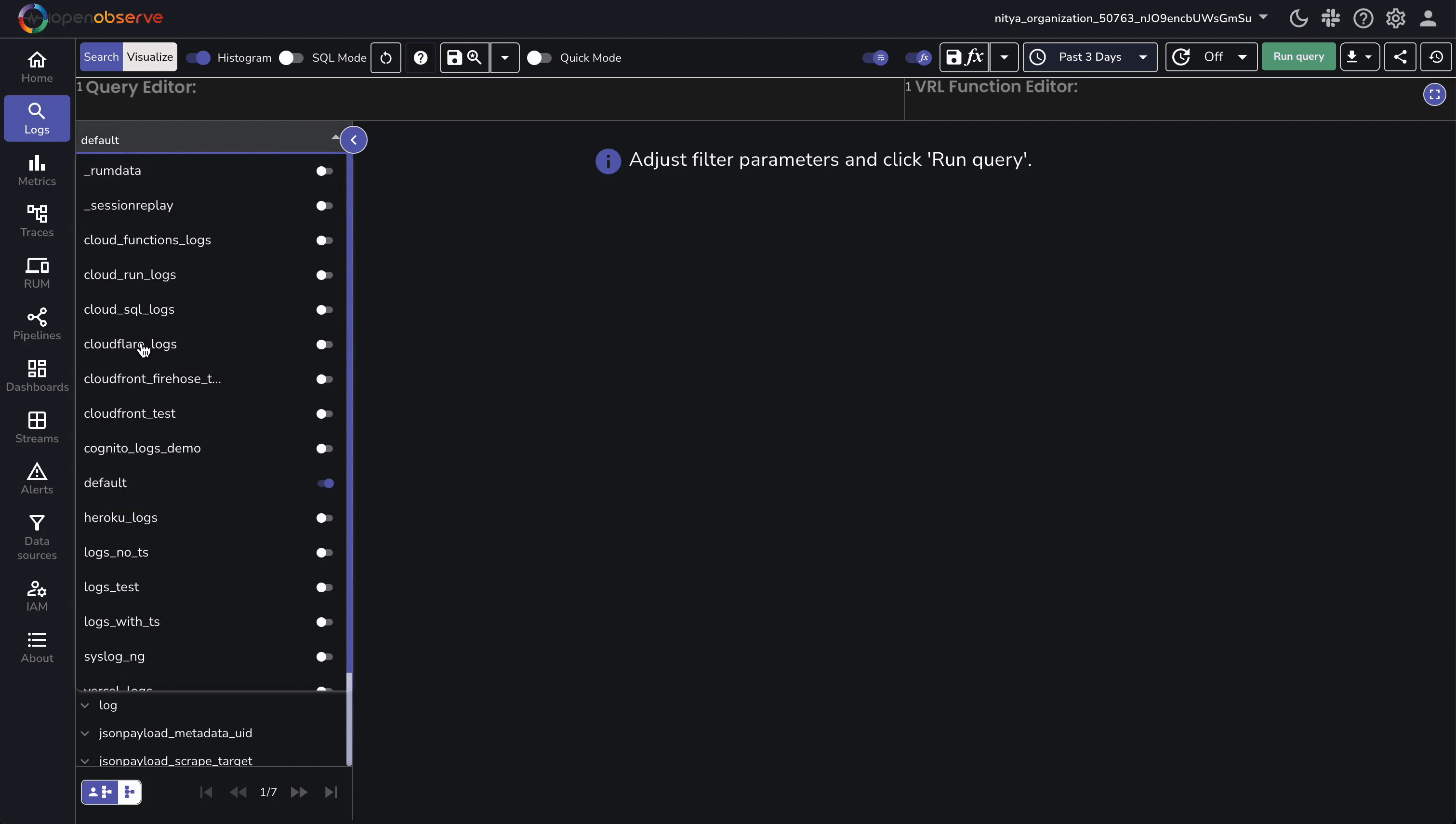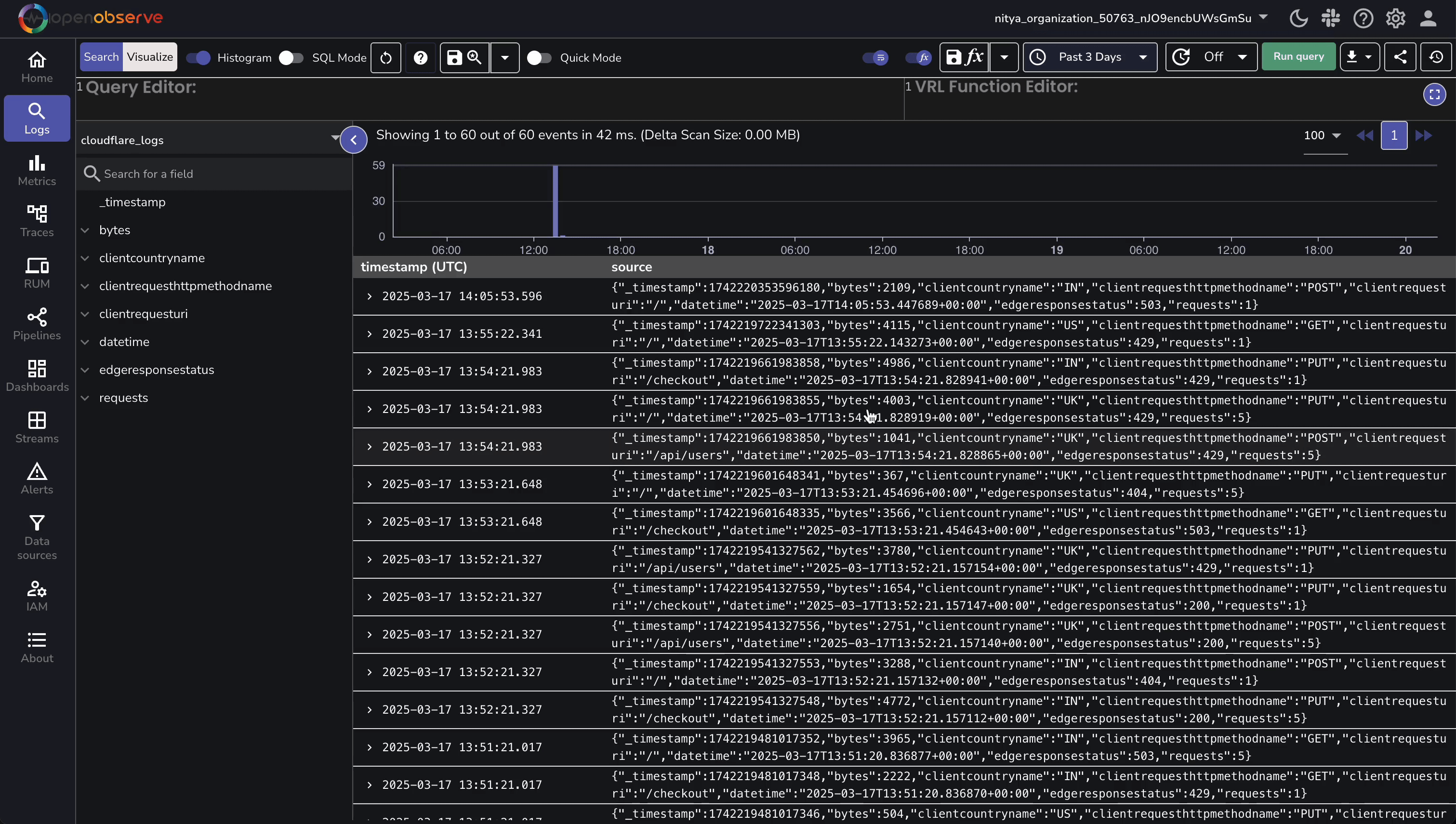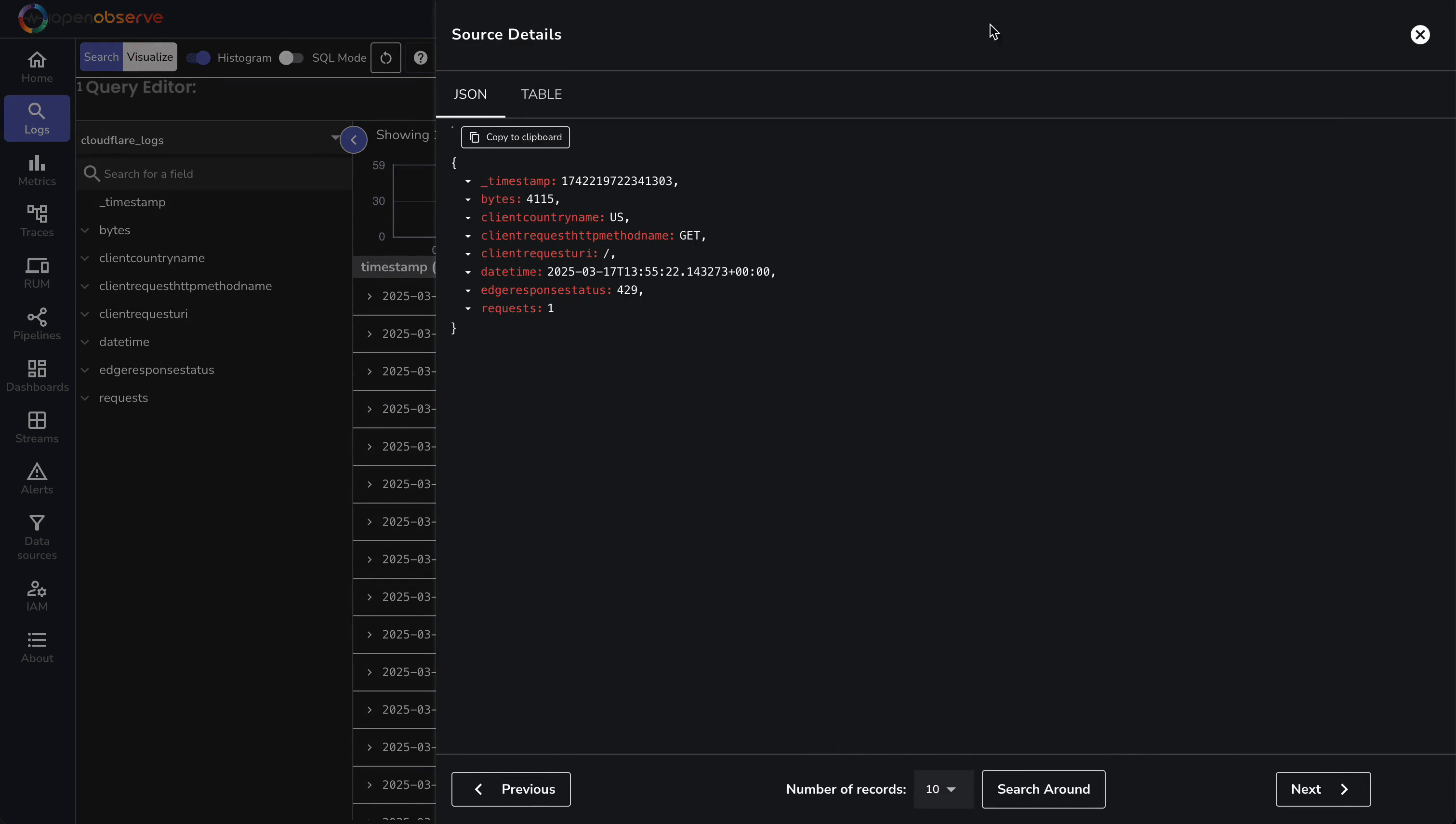
With our GraphQL example, this data is initially simulated, with the real logs following 5-10 minutes later. If you’re using Logpush, you will see instant logs.
You’ve built a robust Cloudflare log monitoring system with OpenObserve, using either the GraphQL API or Logpush to streamline the process. Now, you have deep visibility into your traffic—request details, response codes, and security events—all in one place. Whether you’re on Free, Pro, Business, or Enterprise, this setup allows you to monitor your Cloudflare logs.
With your Cloudflare logs streaming into OpenObserve, you can further process them using pipelines, visualize them using interactive dashboards, or set up custom alerts to proactively assess and mitigate potential issues with your application.
Want to learn more or need assistance? Join our Slack community or reach out directly.